The 2-Tissue (BFM) model implements fitting a two-tissue compartment model in each image pixel. It is based on an analytic solution of the system of differential equations which results in the calculation of two eigenvalues a1 and a2.
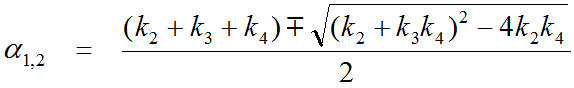
The expected tissue activity is obtained by the convolution of the input function with a sum of two decaying exponentials plus a contribution from whole blood.
![]()
This operational equation which can be fitted to the data has 5 parameters: q1, q2, a1, a2, vB . It is linear in the parameters q1, q2, vB, and nonlinear in a1, a2 . The q1 and q2 parameters are also a combination of the rate constants.
The basis function method by Hong and Fryer [43] performs the data fitting in the following way:
In the case of irreversible binding k4 is assumed to be zero. Hereby the number of fitted parameters is reduced and the operational equation simplifies to
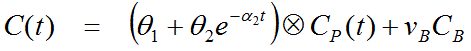
It is notable that in this case only one basis function appears in the equation. Therefore, the number of linear fits is reduce from N2 to N, making pixel-wise fitting very fast.