The PMOD pixel-wise modeling tool (PXMOD) is aimed at the quantitative analysis of functional studies, mainly with Positron Emission Tomography (PET) or Single Photon Emission Tomography (SPECT). Such studies typically result in a sequence of images which monitor the uptake and distribution of an injected tracer over time. The image pixel values represent the average tracer activity concentration (TAC) in tissue throughout the acquisition.
The PXMOD tool provides a set of models which can be applied to each pixel-wise TAC. When a suitable model is chosen, the resulting model parameters quantify a physiologic process such as perfusion or glucose consumption, or a quantity such as the receptor binding potential. Functional maps are created by assembling images from the result parameter values in the individual pixels.
Starting the Pixel-wise Modeling Tool
The pixel-wise modeling tool is started with the PXMod button from the PMOD ToolBox
![]()
or by directly dragging an image file onto the above button.
The PXMOD user interface is organized as shown below after a data set has been processed using the Vt (3 Calc. Methods) model. Note the workspace tabs which allow to work on multiple data sets in parallel. To the right there is a taskbar available providing shortcuts to important functionality.
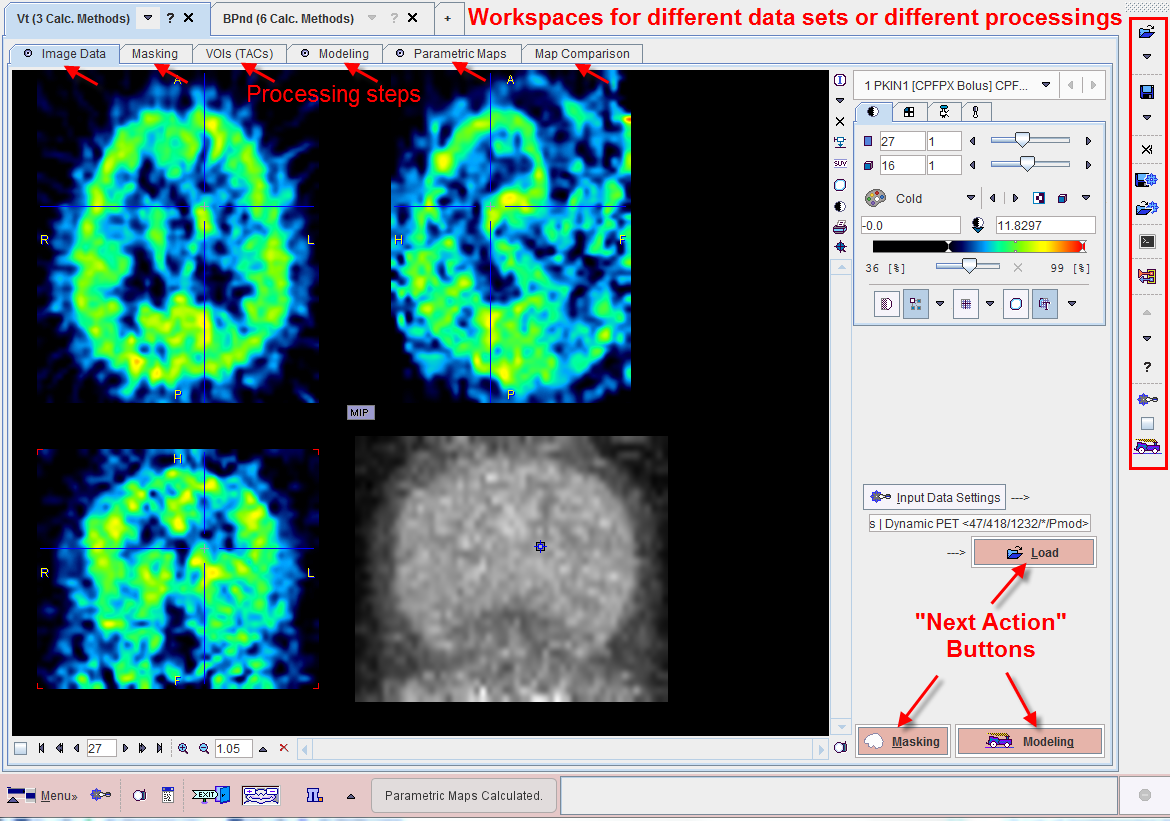
Step-by-Step Processing
PXMOD data processing is based on a step-by-step approach, whereby each step is performed on a separate pane. Once a processing step has been performed, the user moves to the next step using a red action button located in the lower right workspace corner. To go back to a previous step, one of the prior panes can be selected by its tab. If the tasks for all steps have been configured appropriately, the button ![]() in the taskbar can be used for an complete re-processing.
in the taskbar can be used for an complete re-processing.
In contrast to earlier versions of PXMOD the use of transient data data is not supported any longer. Rather, information pieces created during the processing session such as masks or volumes-of-interest (VOIs) need to be saved before they can be applied. Therefore, at the end of a processing session, it is always possible to save the whole processing configuration into a protocol file. The protocol allows to exactly recall all data processing elements for examination, or to repeat a processing with some changes.
Taskbar
The elements in the taskbar have the following functionality which is always directed to the currently selected workspace:
|
Load input image data. The arrow below the load button is used for switching among the available image formats. |
|
Save all parametric maps. The arrow below the load button is used for switching among the image formats which can be used for saving. |
|
Close all input and result images of the selected workspace. |
|
Save the processing session of the selected workspace as a PXMOD protocol file. |
|
Load a PXMOD protocol file (aka configuration settings file) to restore a prior processing session. |
|
Open the batch mode facility. |
|
Send the blood data and all TACs used in preprocessing to the general kinetic modeling tool PKIN (Option). |
|
Switch to the previous/next model configuration in the models list. The list order can be changed in the users configuration facility. |
|
Show a short help information for the currently selected model. |
|
Open a dialog window with the configuration of all processing steps. |
|
If this box is checked, the pixel-wise processing is restricted to the slice currently shown on the Image Data page. |
|
With this button, all intermediate data in the workspace are cleared, and then all processing steps including data loading performed using the current configuration. |
The following sections describe how data is step-wise processed. The models themselves are explained in a separate section.