PMOD Database Functionality
The PMOD database functionality is based on an external SQL database engine. Two such databases are currently supported:
- mySQL is a database which runs on different platforms. While mySQL has been distributed with PMOD for several years, this is no longer the case. However, if you have been running the PMOD database with mySQL you can continue to do so with the mySQL server version 5.0. The mySQL installation is not described in the PMOD Installation Guide.
- JavaDB (also called Derby), an embedded database bundled with Java 6 which requires no installation. The use of JavaDB is encouraged, and at some time point support of mySQL might be suspended.
In this section it is assumed that the database engine is working properly.
There are two different types of databases in PMOD:
- JDBC Databases: These are SQL databases to which PMOD communicates using the Java Data Base Connection (JDBC) interface. Typically, the JDBC Databases reside on the local machine. The user can create new JDBC databases from the PMOD configuration utility. If he wants, he can make them available to PMOD installations on different computers by a PMOD protocol called Transaction Server (TS, see below).
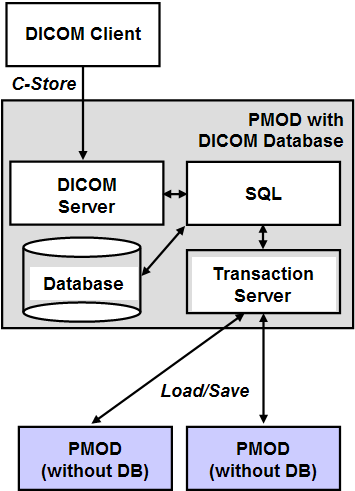
- Remote Transaction Server Databases: These are SQL databases which are not directly accessed, but indirectly through a PMOD installation residing on a different computer. As the transaction server databases are managed by a different PMOD installation, they cannot be created or deleted, but only used for reading and writing.
The transaction server concept is useful in an environment of multiple PMOD installations. On one of the PMOD installations, the PMOD JDBC databases are created. On the same system, the PMOD DICOM server is started, and saves the received images in one of the databases. On all other installations, mySQL need not be installed. Those installations access the databases just through the transaction server as illustrated below.
Note:
After the installation of Pmod3.3, the Pmod database and the DbSvr transaction server are available. PMOD database contains different types of example data, unless the example database was not selected for installation.
The PMOD database default port is 5200.
The DbSvr Transaction server default port is 5100 and database is DbSvr (to avoid conflicts on DB access).
In the configuration panel, to prevent port overlapping, for the new transaction servers, databases ports number higher then 5200 are proposed.
